Medik Blog
Patient positioning involves properly maintaining a patient’s neutral body alignment by preventing hyperextension and extreme lateral rotation to prevent complications of immobility and injury. When positioning a patient in bed, supportive devices such as pillows, rolls, and blankets, along with repositioning, can aid in providing comfort and safety.
Benefits of patient positioning
Patient positioning plays an important role in helping to promote the comfort and safety of patients throughout their hospital stay.
Patient comfort and safety. Promote clear airways for the patient and maintain circulation throughout the procedure (e.g., surgery, examination, specimen collection, and treatment). Impaired venous return to the heart and ventilation-to-perfusion mismatching are common complications. Proper positioning helps keep the patient comfortable while confined to a bed
and minimizes patient exposure during surgery or wound care
Respect for Dignity and Privacy. In surgery, proper positioning helps patients feel their privacy is respected when vulnerable, such as during the perioperative phase.
Optimizing Visibility and Access. In addition to benefiting patients, these positions can also help the healthcare team. Proper positioning can ensure maximum visibility when needing access to a particular body area.
Patient Positions in Medical Bed
Positioning a patient in a medical bed is a common procedure in the hospital. There are various positions possible for patients in bed, which may be determined by their condition, preference, or treatment related to an illness.
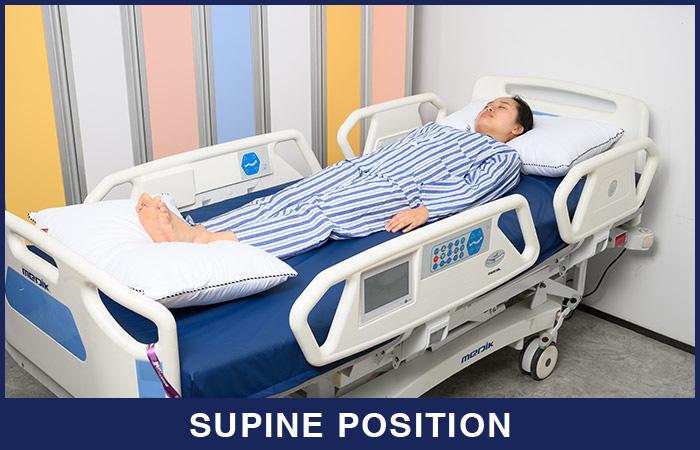
1. Supine position
In supine position, the patient lies flat on back,legs may be extended or slightly bent with arms up or down. Additional support devices may be added for comfort. It provides comfort in general for patients in recovery after some type of surgery.
When the supine position is used:
The supine position is commonly used for general examination or physical assessment. Patients will also need to stay flat after certain procedures, such as a cerebral angiography using the femoral artery.
What to watch out for when using the supine position:
Supine position may put patients at risk for pressure ulcers and nerve damage. Need to check for skin problems and pad bony prominences.
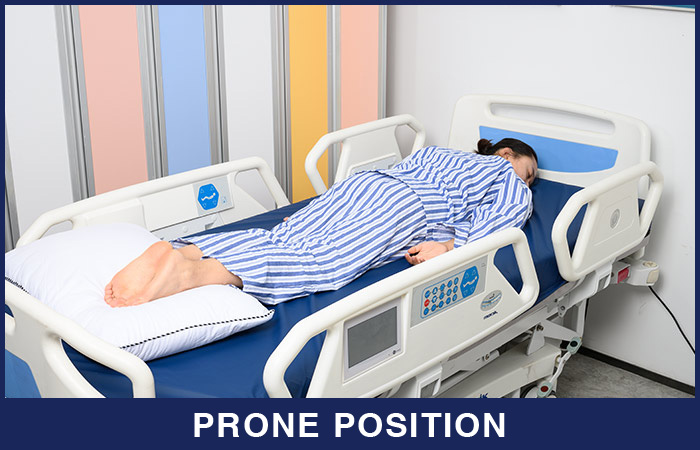
2. Prone position
In prone position, the patient lies on stomach with head turned to the side and the hips are not flexed. To support a patient lying in prone, place a small pillow under the head and a pillow under the legs.
When the prone position is used:
Prone position is used in medical settings to help patients with certain conditions and symptoms get relief. Prone position is the only bed position that allows full extension of the hip and knee joints. It also helps with patients who are unconscious to promote drainage from the mouth. For pediatric patients, the prone position helps with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
What to watch out for when using the prone position:
The pull of gravity on the trunk when the patient lies prone produces marked lordosis or forward curvature of the spine, thus contraindicated for patients with spinal problems. Prone position should only be used when the client’s back is correctly aligned.
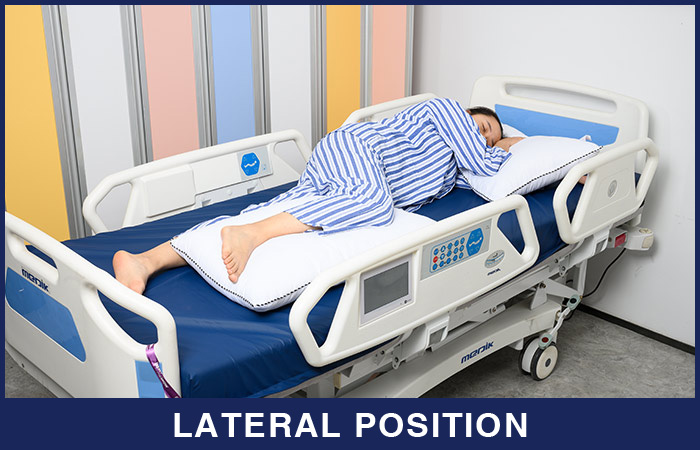
3. Lateral position
The patient lies on the side of the body with the top leg over the bottom leg and the hip and knee flexed. This position helps relieve pressure on the coccyx. Support pillows are needed to correctly position the patient in a lateral position.
When the lateral position is used:
Lateral position used in many different surgeries, particularly those involving the back or hips.
It is likewise used for other non-surgical procedures, such as lumbar punctures and it is additionally used for peripheral nerve blocks of the lower extremity.
What to watch out for when using the lateral position:
Keep an eye on pressure building along the half of the body lying against the surface. You’ll also want to watch for signs of DVT.
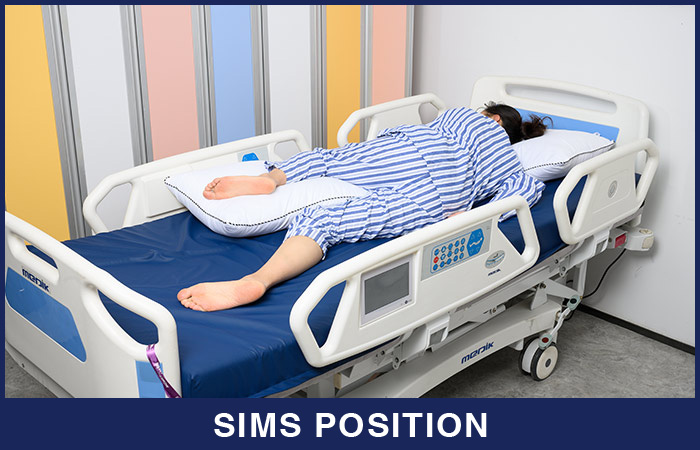
4. Sims position
In the sims position, the patient lies between lateral and prone with legs flexed in front of the patient. The lower arm is positioned behind the client, and the upper arm is flexed at the shoulder and the elbow.
When the prone position is used:
Sims position is usually used for rectal examination, treatments, enemas, and examining women for vaginal wall prolapse.
What to watch out for when using the sims position:
Keep an eye out for pressure injuries on the side of the body lying on the surface and for DVT.
5. Fowler's position
Fowler's position is a standard patient position in which the patient is seated in a semi-sitting position (30-90 degrees) and may have knees either bent or straight. This is a common position to provide patient comfort and care.
There are several Fowler's positions :
* Low Fowler's position: head of the bed raised 15-30 degrees. This position can be used post-procedure, to reduce lower back pain, administer drugs and prevent aspiration during tube feeding.

* Semi Fowler's position: head of the bed raised 30-45 degrees. Semi Fowler’s Position can be used when the patient faces difficulty breathing or is undergoing breathing treatments and when drainage occurs after an abdominoplasty.

* High Fowler's position (Full Fowler's position): head of the bed raised between 60 and 90 degrees. High Fowler's position is usually prescribed to elderly patients as it is scientifically proven to aid in the digestion process and help the patient overcome breathing problems.

What to watch out for when using the Fowler’s position:
Placing an overly large pillow behind the patient’s head may promote the development of neck flexion contractures. Encourage the patient to rest without pillows for a few hours each day to extend the neck fully.
With this position, you should also watch for signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the lower extremities.
6.Trendelenburg position
In Trendelenburg position, patients place the head of the bed lower than the feet. The patient’s arms should be tucked at their sides.
When the Trendelenburg’s position is used:
This position is used in situations such as hypotension and medical emergencies. It helps promote venous return to major organs such as the head and heart.
What to watch out for when using the Trendelenburg’s position:
Trendelenburg’s position is used to provide postural drainage of the basal lung lobes. Watch out for dyspnea, some patients may require only a moderate tilt or a shorter time in this position during postural drainage. Adjust as tolerated.

7.Reverse Trendelenburg Position
Reverse Trendelenburg’s is a patient position that places the head of the bed higher than the feet. It is the opposite of Trendelenburg’s position.
When the reverse Trendelenburg’s position is used:
Reverse trendelenburg is often used for patients with gastrointestinal problems as it helps minimize esophageal reflux.
What to watch out for when using the reverse Trendelenburg’s position:
As a nurse, you will want to watch for signs of deep vein thrombosis or nerve damage in this position.

8. Knee-Chest Position
Knee-chest position can be in a lateral or prone position. In lateral knee-chest position, the patients will be on their side with the legs bent and the knees pulled up toward the chest.
In prone knee-chest position, the patients will kneel with the chest and face on the surface.
When the knee-chest position is used:
Knee-chest position is assumed for a gynecologic or rectal examination.
What to watch out for when using the knee-chest position:
Prone knee-chest position can be embarrassing for some patients. Reassurance and communication can help keep your patient calm and comfortable.
Watch video
References
1. https://nurseslabs.com/patient-positioning/
2. https://nurse.plus/nclex-terminology/terms-abbreviations/fowlers-position/
3. https://healthjade.net/fowlers-position/
4.https://www.osmosis.org/answers/lateral-position